COUNTERS
| CTU- Up Counter | 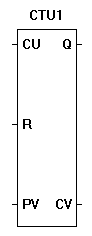 |
| The CTU function is a programmable up counter. A true on CU will cause the counter to increment by one. Once the counter (CV) equals the preset value (CV), the Q output will be true. A true on reset (R) will cause the counter reset to zero and reset the Q output. The down counter triggers on a false to true transition on the CU input. |
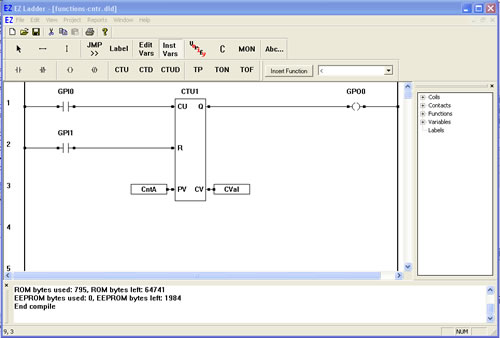
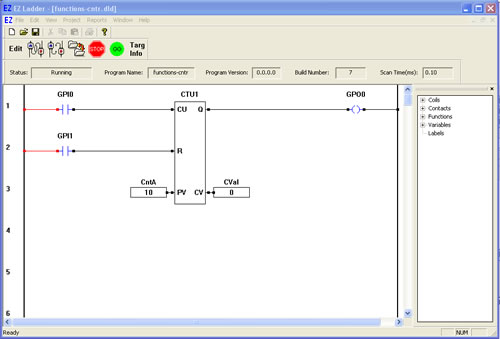
You have completed the CTU exercise.